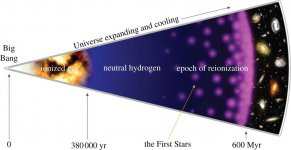
Re the GMTO making the JWST redundant. They serve two different purposes Steve. The JWST is looking in the far infrared region and the reason it is sitting in space with a giant sun shield behind it is so that they can get the (1) sensors to low enough temperature and (2) to remove the atmospherics interfering with the IR imaging to be able to see far enough back in time to within 300 million yrs of the BB - the expanding universe has has pushed these objects deep into the IR optical region due to red shift. We cannot see these from ground based scopes because although we can get the sensors down to very low temps, the atmosphere acts as a an IR blanket ie you cant see this stuff and you have serious thermal noise problems as well. The GMTO OTOH will have superior visible light and near IR gathering capability.
You can download a very nice book about the GMTO here https://giantmagellan.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/GMTScienceBook2018.pdf
You can download a very nice book about the GMTO here https://giantmagellan.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/GMTScienceBook2018.pdf
Last edited:
...the expanding universe has has pushed these objects deep into the IR optical region due to red shift.
Allow me to add this for further clarification:
The visible light emitted by the earliest stars gets shifted into the near-infrared and mid-infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum by the time we see it here and now.
For that reason, to see the first stars and galaxies, we need a powerful near-infrared and mid-infrared telescope, which is exactly what Webb is!
In fact a lot of the Space Probes are starting to look like a waste of time! JWST, I am looking at YOU! 🙁
The general public fantasised that the JWST would return sharp images of distant galaxies and, in that, they were disappointed.
The reality lies in the fact that Webb will study the light from these earliest galaxies by spectrographic analysis, a method which is transparently obvious to the scientists, but opaque to the lay person.
After making ultra-deep near-infrared surveys of the Universe, Webb will follow up with low-resolution spectroscopy and mid-infrared photometry. To study the epoch of reionisation*, high resolution near-infrared spectroscopy will be undertaken.
(*The epoch of reionisation refers to the stage in the universe's development when most of the neutral hydrogen was reionised by the increasing radiation from the first massive stars.)
Attachments
It detects infra that where once visible but now red-shifted. I think it is OK to show picture that is just "shifted back"... Color substitution etc should I think be clearly indicated if it has taken place.
//
//
It's no secret that visual images are created by attaching different colours of the visible spectrum to different frequencies detected outwith that spectrum. We are well-used to this in radio astronomy. It shouldn't be necessary for every false colour image to come with a disclaimer.
What planet(s) do astronomers and astrophysicists come from?Jwst is not for humans to interpret.
I often see the words "false colour image" beneath telescope images in internet articles, so many authors like to stress that fact for the enlightenment of a general audience.
You too, TNT, are a great champion of the ordinary people! 😍
But remember that we are all extraordinary on this thread 🤓
You too, TNT, are a great champion of the ordinary people! 😍
But remember that we are all extraordinary on this thread 🤓
Heck, probably most REPORTERS barely understand what a false-color image is, much less why they are made. "They tell me that otherwise, we wouldn't see anything."I think they should actually.
//
You have to mention false colour because a lot of the sensors don’t show the ‘colour’ they are seeing eg IR or UV. In a digital camera there’s a lot of DSP going on to correct the visible spectrum. I had a Pentax a few yrs ago, and night time photos under certain light had a distinctly green hue to them.
Take example of a wall between radio wave . If the wall doesnot reflects back any radio wave. No mater how much you shift frequency you are never going to detect the wall. The false image you make there is not going to protect you from buldging into the wall.
Yes bulging is not what i thought it was. Crashing into wall would have been more appropriate. Sorry.
To be a great Mathematician or Physicist takes a lot of ego. 😀
I have solved the question of diffraction spikes in hexagonal telescopes like the, and I must be frank here, hopeless JWST.
What idiot came up with this stupid thing? Not me for sure! 🙂
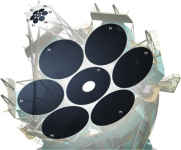
Anywhoo, here's my Engineering and Mathematical thoughts on the Giant Magellan Telescope. It's excellent. I did scratch my head on seven circular mirrors with seven concave (Gregorian) elements in the secondary.
But how it works is there are no diffraction spikes whatsoever. All that happens with 7 circular mirrors ground to within 1/20 th. of a wavelength is you increase light-gathering power over a single 8m mirror.
The predecessor to the GMT was the LBT with adaptive optics:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Large_Binocular_Telescope
One mirror good, two mirrors better. You follow?
As long as you keep phase coherence, it all works nicely:

Now double the circular mirrors:

I leave the seven segment GMT for the interested student. 😎
It's just Fraunhofer Diffraction:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraunhofer_diffraction
I have solved the question of diffraction spikes in hexagonal telescopes like the, and I must be frank here, hopeless JWST.
What idiot came up with this stupid thing? Not me for sure! 🙂
Anywhoo, here's my Engineering and Mathematical thoughts on the Giant Magellan Telescope. It's excellent. I did scratch my head on seven circular mirrors with seven concave (Gregorian) elements in the secondary.
But how it works is there are no diffraction spikes whatsoever. All that happens with 7 circular mirrors ground to within 1/20 th. of a wavelength is you increase light-gathering power over a single 8m mirror.
The predecessor to the GMT was the LBT with adaptive optics:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Large_Binocular_Telescope
One mirror good, two mirrors better. You follow?
As long as you keep phase coherence, it all works nicely:
Now double the circular mirrors:
I leave the seven segment GMT for the interested student. 😎
It's just Fraunhofer Diffraction:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fraunhofer_diffraction
To be a great Mathematician or Physicist takes a lot of ego. 😀
I have solved the question of diffraction spikes in hexagonal telescopes like the, and I must be frank here, hopeless JWST.
One mirror good, two mirrors better. You follow?
Okay, who are ju talking to? Are ju talking to me? Cuzif ju're talking to me, ju bedder get your facts straight cuz I don like it when you don have jor facts straight!!
Last edited:
I did scratch my head on seven circular mirrors with seven concave (Gregorian) elements in the secondary.
I read that the Giant Magellan Telescope is a Gregorian optical-infrared telescope, consisting of a parabolic main light-collecting mirror and a secondary mirror that reflects the image into the lens system. Like the primary mirror, the secondary mirror consists of seven segments, each of which receives the light from the corresponding primary mirror segment.
"Magic Mirrors" is what they're calling them! The glass of each secondary mirror segment is a mere 2 mm thick. Each of the 675 magnets bonded to the rear of each segment is actuated by a computer-driven electromagnetic. This arrangement allows the mirror’s surface to be deformed 2,000 times per second to clean up atmospheric distortions.
Attachments
Wow. So how compromised is this system due to atmospheric influences compared to the JWST over all? Or will it visually outperform it?
Wow...
Locating the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) at high altitude and using adaptive optics certainly diminishes the advantage of a space telescope.
Due to the advance planning time of space missions, the design of the JWST may be regarded as being obsolete.
Remember though, that the two telescopes are designed to perform different functions by operating in different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and that the GMT won't be completed till the end of this decade.
Back in post #10,278, I supplied the following information: "The GMT will have 10 times the light collecting area and four times the spatial resolution of the JWST, and will be 200 times more powerful than any other research telescope currently in use. For context, it will be able to show the torch on a dime from nearly 100 miles away with tack-sharp focus."
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
- Home
- Member Areas
- The Lounge
- What is the Universe expanding into..