Why would or would not the DC resistance of one driver affect the Qts of the other?
Two exactly the same drivers wired in series don't change Qts over a single
unit because the ratio of the variables involved in a calculation remains the
same.
You'll find in books following formulae to calculate TS parameters once
you have recorded impedance vs. frequency.
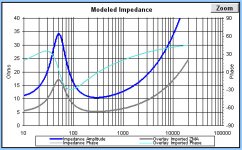
Ro=Rmax/Re; Rmax= max value of Z at Fs
Qms=(Fs*sqrt(Ro))/(F2-F1); F2,F1=frequencies at Rx
Rx=sqrt(Re*Rmax)
Qes=Qms/(Ro-1)
Qts=Qms/Ro
Attachments
Or getting it more simple. For a given input voltage:
1. Two drivers in series - total SPL is the same
2. Two drivers in parallel - total SPL is +6dB
But note that the current in the parallel solution is 4 times the serial. So power is +6dB for the parallel (i.e. 4x).
You don't get nothing for nothing. Matching to amplifier capabilities is more important.
Like this file...🙂
So no matter parallel or series connection, Qts never changes? 🙄
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WvIRsDHFiis
So no matter parallel or series connection, Qts never changes? 🙄
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WvIRsDHFiis
Last edited:
Yes, that is true.But note that the current in the parallel solution is 4 times the serial. So power is +6dB for the parallel (i.e. 4x).
You don't get nothing for nothing.
Yes, that is true also.So no matter parallel or series connection, Qts never changes? 🙄
- Status
- Not open for further replies.