Derivation of E=mc^2:
In one of my batchelor examinations, we, the students, had to
derive E=mc^2.
The Actual Derivation:
In one of my batchelor examinations, we, the students, had to
derive E=mc^2.
The Actual Derivation:
Code:
In this derivation a mass of M (stable mass) is accelerated by a
force to increase its kinetic energy.
Definition of work:
w = f*d (given d and f are in the same direction, otherwise, we
would need a cosine).
The inertial force, f is given by the rate of change of momentum,
which is:
u = mv (momentum)
=>> du/dt = m.dv/dt + v.dm/dt ......... (a)
By definition, du/dt is the force acting on the mass M.
Therefore: dE = (du/dt).dr ( dr being an increment of displacement)
Using (a) in the above:
dE = {m.dv/dt + v.dm/dt}.dr
But dr/dt = v, this will reduce into:
=>> dE = mv.dv + v^2.dm ......... (b)
Now, using the relativistic mass:
m = M/sqrt{1 - (v/c)^2}
Rearranging and squaring:
m^2.{1 - (v/c)^2} = M^2
Differentiating with respect to time t:
2m.dm/dt - d{m^2.v^2/c^2}/dt = 0
=>> 2m.dm/dt - (1/c^2){2mv^2.dm/dt + 2m^2.v.dv/dt} = 0
=>> dm = (1/c^2).{v^2.dm + mv.dv} ..... (c)
Substituting (b) in (c):
dm = (1/c^2).dE
Rearranging:
dE = c^2.dm
Integrating:
E = c^2.{m - M}I knew about the Neutral Kaon and CP violation but hadn't thought how odd it really is.
Others may not be so "in the know" about kaons and CP violation so here's a taster:
It all has to do with the question of whether the laws of nature are the same for matter as they are for antimatter.
If nature treated matter and antimatter alike, then nature would be CP (charge parity) symmetric. If not, CP is violated.
The 'unbalanced' kaon furnishes a prime example of CP violation:
The decays of a neutral kaon occur differently from those of its antiparticle partner, thus violating CP symmetry.
CP violation in kaons is thought to be a good place to look for new physics beyond the standard model.
You have to have a massive Ego to confront the Universe! 🙂
Thus today one of my finer Mathematical solutions.
Problem was nobody could get past this lock.

Caused all sorts of trouble and difficulty. But I knew the answer! Less than 10,000 solutions.
Dialled in a vaguely random 5745 and it opened. Trouble was it wouldn't shut again. We tried oiling it. No. I eventually figured out it hadn't been locked properly in the first place.
No panic. The answer was 5445. Happy Days. A Palindromic solution. They don't teach that at School.
Best Regards from Steve in Portsmouth, UK.
Thus today one of my finer Mathematical solutions.
Problem was nobody could get past this lock.
Caused all sorts of trouble and difficulty. But I knew the answer! Less than 10,000 solutions.
Dialled in a vaguely random 5745 and it opened. Trouble was it wouldn't shut again. We tried oiling it. No. I eventually figured out it hadn't been locked properly in the first place.
No panic. The answer was 5445. Happy Days. A Palindromic solution. They don't teach that at School.
Best Regards from Steve in Portsmouth, UK.
Last edited:
The answer was 5445.
I looked it up, Steve:
The angel number 5445 is a symbol of a man who stands on the ground and has his eyes fixed on the sky.
He is looking for the unknown.
This number indicates the inner depth. It is a bond that connects man with the Universe.
That's you down to a T! 😎
Yes.
You’ve two effects - one from the gravitational field and the other purely from acceleration which changes the clocks inertial frame of reference.
You’ve two effects - one from the gravitational field and the other purely from acceleration which changes the clocks inertial frame of reference.
Last edited:
...you’d also see the clock change if you moved it around due to acceleration.
To allow us to make predictions about how accelerating objects behave, we need to introduce a third postulate to the special theory of relativity.
This is the Clock Postulate that says that an accelerating clock will count out its time in such a way that at any one moment, its timing has slowed by a factor that depends only on its current speed - its acceleration has no effect at all.
In other words, acceleration acts only indirectly by producing a velocity, and the velocity makes the clock run slow by an amount dictated by the Lorentz factor.
None of the choices reflect my hunches. I'm leaning towards the electric universe model for a physical universe, and a holographic universe theory for the overall construction.
The clock postulate is just that, a postulate, but it has been verified experimentally up to extraordinarily high accelerations, as much as 10^18 g.
Bonsai, you mention the clock's "inertial frame of reference". The clock postulate says the accelerated clock's rate is identical to the clock rate in a "momentarily comoving inertial frame" (MCIF). Apparently, this is an inertial frame of reference which happens to be moving with the same instantaneous velocity as the accelerated frame which we're examining at any particular moment!
I found this reference to "Can Special Relativity Handle Acceleration?" which talks about frames of reference:
https://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/Relativity/SR/acceleration.html
Don't ask me to explain it all, as I'm struggling to understand it myself! 🤓
Bonsai, you mention the clock's "inertial frame of reference". The clock postulate says the accelerated clock's rate is identical to the clock rate in a "momentarily comoving inertial frame" (MCIF). Apparently, this is an inertial frame of reference which happens to be moving with the same instantaneous velocity as the accelerated frame which we're examining at any particular moment!
I found this reference to "Can Special Relativity Handle Acceleration?" which talks about frames of reference:
https://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/Relativity/SR/acceleration.html
Don't ask me to explain it all, as I'm struggling to understand it myself! 🤓
One difference between general and special relativity is that in the general theory all frames of reference, including spinning and accelerating frames, are treated on an equal footing. In special relativity accelerating frames are different to inertial frames. Velocities are relative but acceleration is treated as absolute. In general relativity all motion is relative. To accommodate this change, general relativity has to use curved space-time. In special relativity space-time is always flat.
Nice link Galu 👍 The way I understand it is by way of an example like this:-
Imagine two atomic clocks next to each other coasting through space without any gravity field. They are in the same inertial frame. If you apply a force to one (clock 1) it accelerates away from the other - call it clock 2 (during acceleration clock 1 is no longer considered to be an inertial frame). Snapshots of clock 1‘s count rate during acceleration reveal that it is reducing wrt clock 2. When you remove the accelerating force from clock 1, it is now in a new (different) inertial frame compared to clock 2 and it coasts along. Crucially, the time it displays is now lower than clock 2 and will continue to diverge from clock 2. An observer sitting on clock 1 would see clock 2 speed up. Conversely, an observer on clock 2 would see clock 1 slow down (Assume we can see each others time with no delay - impossible in reality of course).
Imagine two atomic clocks next to each other coasting through space without any gravity field. They are in the same inertial frame. If you apply a force to one (clock 1) it accelerates away from the other - call it clock 2 (during acceleration clock 1 is no longer considered to be an inertial frame). Snapshots of clock 1‘s count rate during acceleration reveal that it is reducing wrt clock 2. When you remove the accelerating force from clock 1, it is now in a new (different) inertial frame compared to clock 2 and it coasts along. Crucially, the time it displays is now lower than clock 2 and will continue to diverge from clock 2. An observer sitting on clock 1 would see clock 2 speed up. Conversely, an observer on clock 2 would see clock 1 slow down (Assume we can see each others time with no delay - impossible in reality of course).
Last edited:
If you take an atomic clock and move it around physically ie walk around the lab with it, you can see the time change. One of the posters here a year or so back (billshurv?) talks about seeing a movie clip about it. No doubt if you were in deep space with near enough zero gravity field, you’d also see the clock change if you moved it around due to acceleration.
Sooo elementary Watson. I wonder, did Einstein see this in his mind's eye and do the math, or vice versa?Nice link Galu 👍 The way I understand it is by way of an example like this:-
Imagine two atomic clocks next to each other coasting through space without any gravity field. They are in the same inertial frame. If you apply a force to one (clock 1) it accelerates away from the other - call it clock 2 (during acceleration clock 1 is no longer considered to be an inertial frame). Snapshots of clock 1‘s count rate during acceleration reveal that it is reducing wrt clock 2. When you remove the accelerating force from clock 1, it is now in a new (different) inertial frame compared to clock 2 and it coasts along. Crucially, the time it displays is now lower than clock 2 and will continue to diverge from clock 2. An observer sitting on clock 1 would see clock 2 speed up. Conversely, an observer on clock 2 would see clock 1 slow down (Assume we can see each others time with no delay - impossible in reality of course).
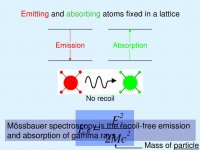
The Mossbauer effect is incredibly exact...
I've been looking into that exactness! 😎
The Mössbauer effect is also called "recoil-free gamma-ray resonance absorption".
The effect results in the production of gamma rays of precisely defined frequency, making it a very useful tool in experimental physics.
For example, the high precision has made possible a direct demonstration of the gravitational red-shift; i.e., the change in the energy of a quantum of electromagnetic radiation as it moves through a gravitational field.
More about the Mössbauer effect and its applications here: https://www.britannica.com/science/Mossbauer-effect/Applications
Attachments
In the presentation about GR I linked to earlier there is a hint about this and in other texts on the subject. He deduced most of the fundamentals intuitively using thought experiments and then did the math. He said deriving the field equations for GR was the hardest thing he ever did.Sooo elementary Watson. I wonder, did Einstein see this in his mind's eye and do the math, or vice versa?
I guess if you had a mathematician of the stature of David Hilbert digging you in the ribs and telling you he new how to do it, it would focus the mind a bit! It took Einstein 2 or 3 attempts over a few week period to convince the German Academy of Sciences that he had it right and on 2 of those occasions Hilbert, in the audience, apparently looked at him and shook his head. He got the 'Hilbert nod' on the third go.
I want ask the probability enthusiasts one question.
If you are standing in a row of 5 people standing side by side. One gunman infront of you has to shoot at you lot. He has only one bullet. What will you do.
1) rely on probability
2) ask gunman to have mercy .
If you are standing in a row of 5 people standing side by side. One gunman infront of you has to shoot at you lot. He has only one bullet. What will you do.
1) rely on probability
2) ask gunman to have mercy .
I guess if you had a mathematician of the stature of David Hilbert digging you in the ribs...
Mathematician Hilbert obviously had physicists summed up!
Attachments
David Hilbert was responsible for the concept of Hilbert Space.
This is a mathematical space which is used to understand and study non-relativistic quantum mechanics.
Since Hilbert Space is an infinite-dimensioned space, I have no hope of understanding the associated mathematics.
There is, however, some connection with the Tesseract! 😉
This is a mathematical space which is used to understand and study non-relativistic quantum mechanics.
Since Hilbert Space is an infinite-dimensioned space, I have no hope of understanding the associated mathematics.
There is, however, some connection with the Tesseract! 😉
Attachments
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
- Home
- Member Areas
- The Lounge
- What is the Universe expanding into..