First I want to say this is a public diy forum, we share what we know and what we have learned, if you don´t want to share what you know, please leave this forum. Many people have leaved this part of the forum, and I will also do that, because here are very little new ideas, what people are doing today is just repeating of what other people have done many years ago. The only difference is that we have more high resolution lcd:s today, but in the same time commercialprojectors have been very cheap with the same resolution and better contrastrate.
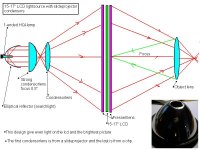
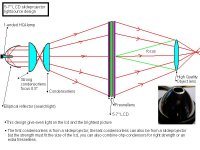
I have here collected the most common projectorplans, some are cheap and some are more expensive to build. The difference in light output between the designs is about 40%. There is not such thing like 2-3 times brightness, if you get 2-3 times more lightoutput you have used wrong condensorlenses from the beginning.
Please share your projectorplans here and help me complete this
collection!!!
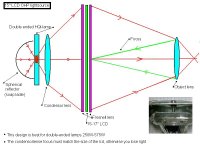
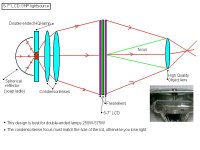
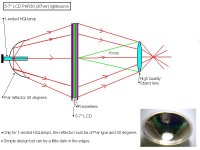
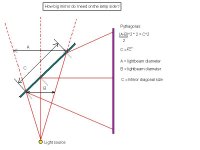
This projector design is the most common and use the parts from an ohp-projector, works with 250-575W double ended lamps. 65% of the light from the lamp will hit the fresnel.
I have here collected the most common projectorplans, some are cheap and some are more expensive to build. The difference in light output between the designs is about 40%. There is not such thing like 2-3 times brightness, if you get 2-3 times more lightoutput you have used wrong condensorlenses from the beginning.
Please share your projectorplans here and help me complete this
collection!!!
This projector design is the most common and use the parts from an ohp-projector, works with 250-575W double ended lamps. 65% of the light from the lamp will hit the fresnel.
Attachments
Great idee!!!! nice overview. Maybe we have to find examples of the specific projectors and also post them as examples.
In your pictures you say that the focal length of the objective is the same as the distance to the lcd, but i believe that it has to be just a little bit longer (240 mm objective ---> ~260 mm distance from tft to objective.)
I still wanna try the design of two half parabolic mirrors and a spherical one.
Maybe i will buy a raylight and test it.
In your pictures you say that the focal length of the objective is the same as the distance to the lcd, but i believe that it has to be just a little bit longer (240 mm objective ---> ~260 mm distance from tft to objective.)
I still wanna try the design of two half parabolic mirrors and a spherical one.
An externally hosted image should be here but it was not working when we last tested it.
Maybe i will buy a raylight and test it.
An externally hosted image should be here but it was not working when we last tested it.
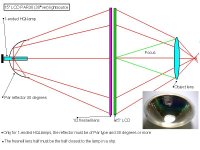
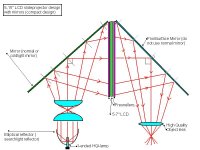
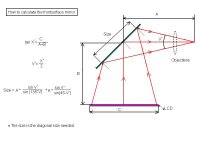
Here is the most advanced projectordesign plans and also most compact, but most expensive. As you can see you must have pretty big mirrors if you want it most compact. You can use smaller mirrors if you move them closer to the lamp / object, but the distance will be bigger = bigger projector. You can use normal glass mirror on the lamp side, it can also be coldmirror to reduce the heat, but you can also have coldmirror build in to the lamp reflector (cheaper and more easy). The mirror on the objectlens side must be a frontsurface mirror otherwise you get ghosting, you can find these in ohp-projectors.
Attachments
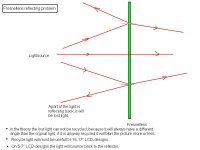
Mirrors are good, but what size do I need ?
In small lcd designs 5-7" you can not use so much smaller mirrors than the lcd size depending on that the light from the condensors lenses are almost parallel. But in 15-17" you can use much smaller mirrors than the lcd.
In small lcd designs 5-7" you can not use so much smaller mirrors than the lcd size depending on that the light from the condensors lenses are almost parallel. But in 15-17" you can use much smaller mirrors than the lcd.
Attachments
In small lcd designs 5-7" you can not use so much smaller mirrors than the lcd size depending on that the light from the condensors lenses are almost parallel.
Not true, it depends how far you place the mirror from the lcd, just like how the ohp's mirror is so far away wich in turn alows it to be small.
Actually,
I think you are both right. The real problem with lens schematics is that they are so oversimplified as to be almost misleading. There are usually many millions of light paths through the lens. And there will rarely if ever be one simple scheme or focal point. The best you can hope for is to get most of the light to a common focal point. The fact is that positive plano lenses or similar lenses collapse the light beam no matter which way they are oriented. So where the light focuses depends on the angle of the light. However there is a light reflection issue which sometimes effects the orientation of the lens because the closer the light ray is to perpendicular to the surface it enters (or perpendicular to the tangent of a curved surface) the less light will be reflected back. So that is why there are often preferred orientations. The higher the angular incidence that the light ray hits the surface more light is reflected up to a maximum amount of reflection that is specific for each substance. This angle is usually around forty five (but not exactly) degrees for many types of glass.
For this reason you will almost always see the first positive surfaces of lenses rather large curved so that the light rays coming from larger angles hit the lens surface at a more desirable angle thus reflecting less light back.
Hezz
I think you are both right. The real problem with lens schematics is that they are so oversimplified as to be almost misleading. There are usually many millions of light paths through the lens. And there will rarely if ever be one simple scheme or focal point. The best you can hope for is to get most of the light to a common focal point. The fact is that positive plano lenses or similar lenses collapse the light beam no matter which way they are oriented. So where the light focuses depends on the angle of the light. However there is a light reflection issue which sometimes effects the orientation of the lens because the closer the light ray is to perpendicular to the surface it enters (or perpendicular to the tangent of a curved surface) the less light will be reflected back. So that is why there are often preferred orientations. The higher the angular incidence that the light ray hits the surface more light is reflected up to a maximum amount of reflection that is specific for each substance. This angle is usually around forty five (but not exactly) degrees for many types of glass.
For this reason you will almost always see the first positive surfaces of lenses rather large curved so that the light rays coming from larger angles hit the lens surface at a more desirable angle thus reflecting less light back.
Hezz
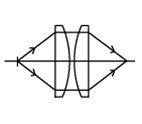
mathias, i hate to disapoint you but your drawings are wrong with the condensers lol
Like Hezz say we are both right, and my drawings are NOT wrong, if you have parallel light coming from the lamp they work in the way I have drawn. You have a POINT source and then they work in the way you show .
However there is a light reflection issue which sometimes effects the orientation of the lens because the closer the light ray is to perpendicular to the surface it enters (or perpendicular to the tangent of a curved surface) the less light will be reflected back. So that is why there are often preferred orientations. The higher the angular incidence that the light ray hits the surface more light is reflected up to a maximum amount of reflection that is specific for each substance. This angle is usually around forty five (but not exactly) degrees for many types of glass.
Hezz and thats exactly right, and its why ive got my condensers coated in anti glare, the anti glare have a much sharper light then with the same without the anti glare, the one with the anti glare is somewhat brighter too as more light is going where we want it.
As for the angles thats where reflectors come in, its not just a matter of getting a spherical reflector, the focal is very important to obtain maximum light from the bulbs light transmision pattern, to get the desired angle through the condenser, and to the frensel at your desired focals for maximum efientcy at the coresponding angles required, even the depth of a spherical reflector matters to get the ultimate desired results.
Trev
Trev
if you have parallel light coming from the lamp they work in the way I have drawn. You have a POINT source and then they work in the way you show
Im not talking about the paralelle light ones, i am talking about the point source pics otherwise i wouldnt have posted the way 2 condensers work with a point source.
Also hezz is talking about miss matched light, there is no way u will get rays out of a positive power lens in the way you show it, paralelle or non paralelle light, the light will go to the focal point of the lens.
Trev
Trev, all drawings use the technics from professional design and I don´t understand why you say they don´t work.
Many of the designs is taken from physics books, and I promise you that they don´t have wrong! The ellipticalreflector design is used in all modern slideprojectors with a lamp of the type ELC A1/259 with built in reflector. And the other designs use the normal ohp-design.
And if you say these design are wrong I suggest that you draw a right one.
Many of the designs is taken from physics books, and I promise you that they don´t have wrong! The ellipticalreflector design is used in all modern slideprojectors with a lamp of the type ELC A1/259 with built in reflector. And the other designs use the normal ohp-design.
And if you say these design are wrong I suggest that you draw a right one.
Mathias this stuff has been posted in here a few times and argued about before, i dont have time right now to draw up a pic but i will do abit later on as i have some serious work to do and not enough time. Have a read in here. there are manny formulas and they tell u how basic lenses work, although imo not for the beginner.
http://www.edmundoptics.com/TechSupport/DisplayArticle.cfm?articleid=267
You can always ring them, ive rung them up before, they are more then willing to help and are all optical engineers.
Trev
http://www.edmundoptics.com/TechSupport/DisplayArticle.cfm?articleid=267
You can always ring them, ive rung them up before, they are more then willing to help and are all optical engineers.
Trev
- Status
- This old topic is closed. If you want to reopen this topic, contact a moderator using the "Report Post" button.
- Home
- General Interest
- Everything Else
- The Moving Image
- Optics
- DIY-Projector Plans and theory collection !!